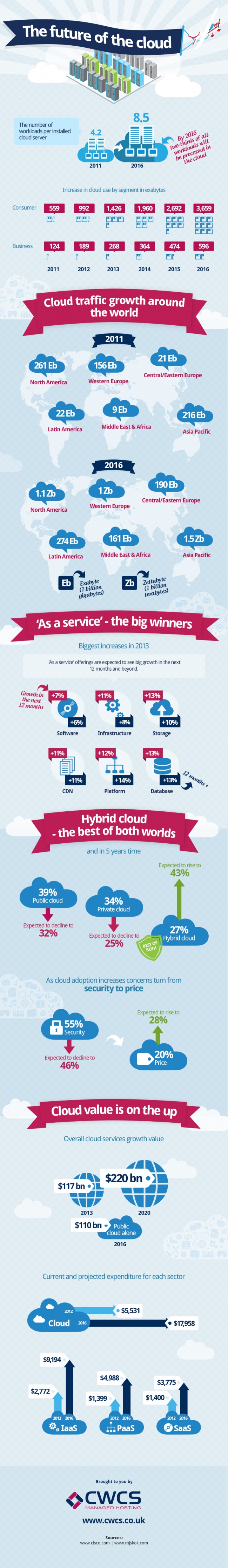
Big data describes the large volume of both unstructured and structured data which is not handled by traditional database. Big data usually includes data sets with sizes beyond the ability of commonly used software tools to capture, curate, manage, and process the data within time. Technology is changing the way financial institutions operate, markets are organized, and consumers and businesses interact with investment banks. It will also offer insight on the struggle between regulation and adopting smarter operations for demanding clients. It will offer new ideas for technology and information executives on the next wave of innovation – not only what banks are doing today, but what they are planning for tomorrow.
Ready access to data, quickly and with rich analysis and visualization, has qualitatively, as well as quantitatively, changed the communication patterns and hence the decision processes in many Technologies. Business intelligence software provides actionable and manageable information that can improve chain’s efficiency—from manufacturer through to the end-user. The goal of big data management is to ensure a high level of data quality and accessibility for business big data analytics applications and intelligence. The primary objective of analyzing big data is to support organizations in making better business decisions.
End-to-End Visibility –
Business intelligence software can provide far greater transparency by handling big data correctly. Business intelligence creates improved end-to-end transparency, and provides access to the inner workings of a business.
Avoid vendor lock-in and fragmented solutions -
Data proliferation demands innovative infrastructure, self-service analytics access and effective management. Big data solution providers address a fraction of the hardware stack or make you rip and replace your infrastructure.
Data organization-
Data has become most powerful resource for any business, especially for eCommerce stores, it’s a daunting task to collect data from multiple sources and organize it in a way that it gives useful information to business owners. Big data provides solution to all the challenges of data handling and also helps in analyzing data for making better business decisions.
Better Collaboration -
Collaboration is the fundamental rule of logistics management: if one link in the chain is severed, the entire process can fall apart. Building relationship after relationship is a fundamental step in the supply chain, which is used to make better collaboration one of the most important ways that big data influences the supply chain market. Business intelligence, and the software that comes with it, makes maintaining supplier-buyer relationships simple.
Pinpoint Focus –
Big data provides real time updates and insights, which is essential to achieving better focus. As you receive that intelligence, you can make any business changes necessary, large or small, to exact specifications.
Here are some examples of a combination of different tools for big data insights:
- Cloud is extensible, scalable, flexible, elastic, self-healing, on-demand, etc. and used to provide the inexpensive hardware/software platform with all applications (such as Kapow, SAP Intelligence Analysis for Public Sector application by Palantir, SAP, Sybase IQ, CRM, SAP Data Services with text analytics) for rapid ramp-up at lower capital cost requirements.
- Hadoop provides reliable data storage and high-performance parallel data processing – the ability to store extremely large data sets.
- SAP HANA provides the extremely accelerated business warehouse/enterprise data warehouse.
About the Author:
Vaishnavi Agrawal loves pursuing excellence through writing and have a passion for technology. She has successfully managed and run personal technology magazines and websites. She currently writes for intellipaat.com, a global training company that provides e-learning and professional certification training.
The courses offered by Intellipaat address the unique needs of working professionals. She is based out of Bangalore and has an experience of 5 years in the field of content writing and blogging. Her work has been published on various sites related to Big Data, Business Intelligence, Project Management, Cloud Computing, IT, SAP, Project Management and more.